
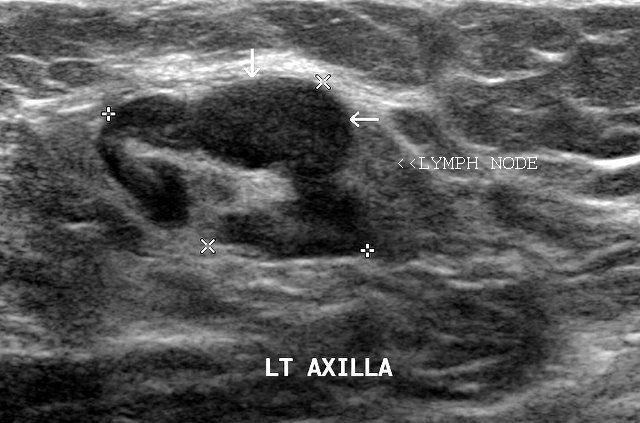
The course of treatment depends on the type of lymphoma a person has and the stage it has reached. Share on Pinterest Chemotherapy is one of the possible treatments that doctors may use to treat lymphoma. As cancerous lymphocytes spread into other tissues, the immune system cannot defend against infections as effectively. Lymphoma can spread rapidly from the lymph nodes to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system. Pain, weakness, paralysis, or altered sensation may occur if an enlarged lymph node presses against spinal nerves or the spinal cord. Some additional symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma include: pain in lymph nodes after drinking alcohol.Other symptoms of both types of lymphoma may include: Anyone who has persistently swollen glands should see their doctor for a consultation.

The overlap of symptoms can lead to misdiagnosis. Pain is also more likely to accompany the swelling if it has occurred due to an infection. In lymphoma, the swelling does not resolve. Lymph nodes can also swell during common infections, such as a cold. Some people confuse lymphoma with back pain. They may become painful if the enlarged glands press on organs, bones, and other structures. Swelling often occurs in the neck, groin, abdomen, or armpits. There are lymph nodes all around the body. Others may notice a swelling of the lymph nodes. Some people will not experience any symptoms. However, they typically continue for a more extended period. The symptoms of lymphoma are similar to those of some viral diseases, such as the common cold. will receive a diagnosis in their lifetime. The NCI estimate that Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for 0.5% of all cancers and approximately 0.2% of people in the U.S. In people with Hodgkin lymphoma, the cancer usually moves from one lymph node to an adjacent one. Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of the immune system, and doctors can identify it by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which are abnormally large B lymphocytes. Tumor growth in non-Hodgkin lymphoma may not affect every lymph node, often skipping some and growing on others.Īccording to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), non-Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for 4.2% of all cancers in the United States, and a person’s lifetime risk of developing it is about 2.2%. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is the most common type, typically develops from B and T lymphocytes (cells) in the lymph nodes or tissues throughout the body. Share on Pinterest Swollen glands that do not go away can be a sign of lymphoma.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
